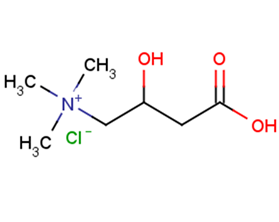
DL-Carnitine HCl
CAS No. 461-05-2
DL-Carnitine HCl( DL-Carnitine chloride )
Catalog No. M18566 CAS No. 461-05-2
DL-Carnitine HCl is a quaternary ammonium compound biosynthesized from the amino acids lysine and methionine.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 37 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDL-Carnitine HCl
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDL-Carnitine HCl is a quaternary ammonium compound biosynthesized from the amino acids lysine and methionine.
-
DescriptionDL-Carnitine HCl is a quaternary ammonium compound biosynthesized from the amino acids lysine and methionine.(In Vitro):The main role of L-carnitine is to shuttle long-chain fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane. After L-carnitine and acyl-CoA become acyl-carnitine by activation of carnitine palmitoyl transferase (CPT)-I, the transported acyl-carnitine is changed into acyl-CoA by CPT-II in the mitochondria matrix. Palmitoyl-CoA-induced mitochondrial respiration is increased by L-carnitine treatment, and then is accelerated by the presence of ADP. This acceleration is induced by treatment with L-carnitine in a concentration-dependent manner, and is saturated at 5 mM L-carnitine. Pretreatment with L-carnitine augments Nrf2 nuclear translocation, DNA binding activity and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expression in H2O2-treated HL7702 cells. L-carnitine protects HL7702 cells against H2O2-induced cell damage through Akt-mediated activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway.(In Vivo):L-carnitine is found to down-regulate the ubiquitin proteasome pathway and increase IGF-1 concentrations in animal models. L-carnitine administration for 2 weeks of hindlimb suspension alleviates the decrease in weight and fiber size in the soleus muscle. In addition, L-carnitine suppresses atrogin-1 mRNA expression, which has been reported to play a pivotal role in muscle atrophy. Simultaneous treatment with L-carnitine attenuates the renal fibrosis (which correlated with a reduction of plasma TGF-β1 levels) and the pro-oxidative and proinflammatory status reported in L-NAME groups, with a concomitant increase in the expression of PPAR-γ.
-
In VitroThe main role of L-carnitine is to shuttle long-chain fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane. After L-carnitine and acyl-CoA become acyl-carnitine by activation of carnitine palmitoyl transferase (CPT)-I, the transported acyl-carnitine is changed into acyl-CoA by CPT-II in the mitochondria matrix. Palmitoyl-CoA-induced mitochondrial respiration is increased by L-carnitine treatment, and then is accelerated by the presence of ADP. This acceleration is induced by treatment with L-carnitine in a concentration-dependent manner, and is saturated at 5 mM L-carnitine. Pretreatment with L-carnitine augments Nrf2 nuclear translocation, DNA binding activity and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expression in H2O2-treated HL7702 cells. L-carnitine protects HL7702 cells against H2O2-induced cell damage through Akt-mediated activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway.
-
In VivoL-carnitine is found to down-regulate the ubiquitin proteasome pathway and increase IGF-1 concentrations in animal models. L-carnitine administration for 2 weeks of hindlimb suspension alleviates the decrease in weight and fiber size in the soleus muscle. In addition, L-carnitine suppresses atrogin-1 mRNA expression, which has been reported to play a pivotal role in muscle atrophy. Simultaneous treatment with L-carnitine attenuates the renal fibrosis (which correlated with a reduction of plasma TGF-β1 levels) and the pro-oxidative and proinflammatory status reported in L-NAME groups, with a concomitant increase in the expression of PPAR-γ.
-
SynonymsDL-Carnitine chloride
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number461-05-2
-
Formula Weight197.66
-
Molecular FormulaC7H15NO3·HCl
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityH2O : ≥ 33 mg/mL; 166.95 mM
-
SMILES[Cl-].C[N+](C)(C)CC(O)CC(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
(iso)-T 448
——
-
Ethyl icosanoate
Ethyl icosanoate (Ethyl arachidate) is a compound extracted from the rectal glands of the female B. correcta.
-
HSV-1-amide UL 26 Op...
HSV-1 Protease substrate is a peptide substrate for HSV-1 (Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1) protease, and the specificity constant (kcat/Km) at pH 7.5 for cleavage is 5.2 M-1 s-1.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


